Pulse of Information
Your source for the latest insights and updates.
Food Poisoning Fiasco: A Recipe for Regret
Discover the shocking truth behind food poisoning disasters and learn how to avoid your own recipe for regret!
Top 10 Common Causes of Food Poisoning You Should Avoid
Food poisoning is a serious issue that can lead to various gastrointestinal problems and, in severe cases, hospitalization. Understanding the top 10 common causes of food poisoning is essential for anyone who wants to enjoy safe eating and cooking practices. The first culprit is undercooked meat, which can harbor harmful bacteria such as Salmonella and E. coli. Always ensure your meat is cooked to the appropriate temperature to eliminate these pathogens.
Another common cause is cross-contamination, which occurs when raw foods come into contact with cooked or ready-to-eat items. This can happen through kitchen utensils, cutting boards, or hands. Additionally, consuming unpasteurized dairy products can expose you to Listeria, while improper food storage, particularly leaving perishable items at room temperature, can lead to rapid bacterial growth. By being aware of these hazards, you can significantly reduce your risk of food poisoning.
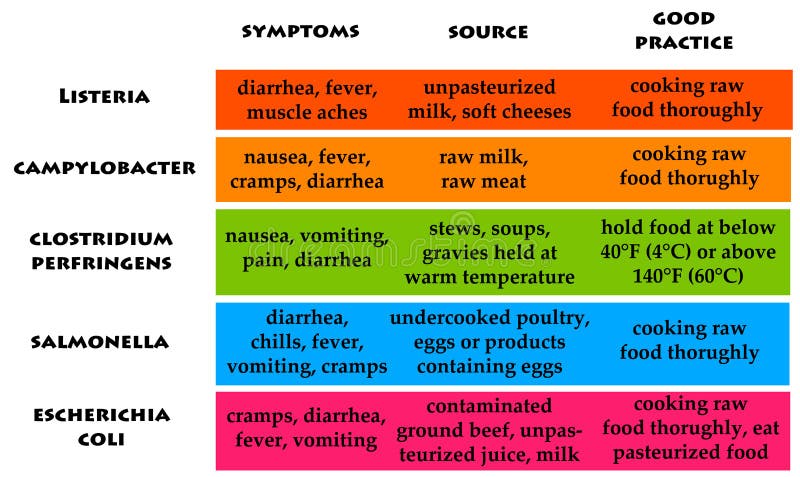
How to Safely Handle and Prepare Food to Prevent Illness
Handling and preparing food safely is crucial to prevent foodborne illnesses. To start with, always ensure that your hands are clean by washing them with soap and water for at least 20 seconds before handling any food. This simple step is essential, as it reduces the likelihood of transferring harmful bacteria from your hands to the food. Additionally, use clean utensils, cutting boards, and surfaces to avoid cross-contamination. It is advisable to separate raw meats from other foods, especially ready-to-eat items, to prevent the spread of pathogens. Always remember to wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before consumption.
When it comes to cooking, it is important to use a food thermometer to ensure that food reaches the appropriate internal temperature. For instance, poultry should be cooked to an internal temperature of 165°F (75°C). After cooking, allow food to cool before storing it in the refrigerator to minimize the risk of bacteria growth. Furthermore, leftovers should be consumed or refrigerated within two hours to maintain safety. Following these guidelines not only helps in providing delicious meals but also plays a vital role in preventing foodborne illnesses effectively.
What Are the Symptoms of Food Poisoning and When Should You Seek Help?
Food poisoning is a common yet potentially serious condition caused by consuming contaminated food or beverages. The symptoms of food poisoning can vary depending on the source of contamination but typically include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Symptoms may manifest within hours to days after ingestion and can range from mild to severe. It is essential to be aware of these symptoms to take appropriate action and prevent further health complications.
If you experience any severe symptoms such as persistent vomiting, high fever (over 101.5°F), blood in your stools, or signs of dehydration (such as dry mouth, dizziness, or decreased urine output), it's crucial to seek help immediately. Additionally, high-risk groups such as pregnant women, infants, elderly individuals, and those with weakened immune systems should consult a healthcare professional even for mild symptoms, as they may be more susceptible to severe complications from food poisoning.