Pulse of Information
Your source for the latest insights and updates.
Machine Learning: When Algorithms Get Smarter Than Us
Discover the mind-blowing world of machine learning and explore when algorithms outsmart humanity. Are we ready for this AI revolution?
The Evolution of Machine Learning: How Algorithms Surpass Human Intelligence
The evolution of machine learning has been a transformative journey over the last few decades, transitioning from simple algorithms that could perform basic tasks to sophisticated models that can analyze vast amounts of data. Early developments focused on rule-based systems, which required extensive human intervention to operate. However, with advancements in computational power and data availability, machine learning algorithms began to learn from their experiences, creating a paradigm shift in how machines interact with data. This learning capability allows algorithms to surpass human intelligence in various domains, including image and speech recognition, where large datasets can be processed faster and more accurately than a human can comprehend.
As we delve deeper into the realm of artificial intelligence, it becomes increasingly evident that machine learning algorithms are evolving at a pace that challenges human cognitive abilities. Modern innovations, such as deep learning, utilize complex multilayered neural networks to uncover patterns in data that are often imperceptible to human analysts. For instance, in medical diagnostics, algorithms can analyze thousands of images, identifying anomalies with precision that oftentimes exceeds that of trained professionals. This melding of technology with machine intelligence highlights not only the capability of algorithms to outperform humans in specific tasks but also emphasizes the necessity for us to adapt to this rapidly changing landscape.
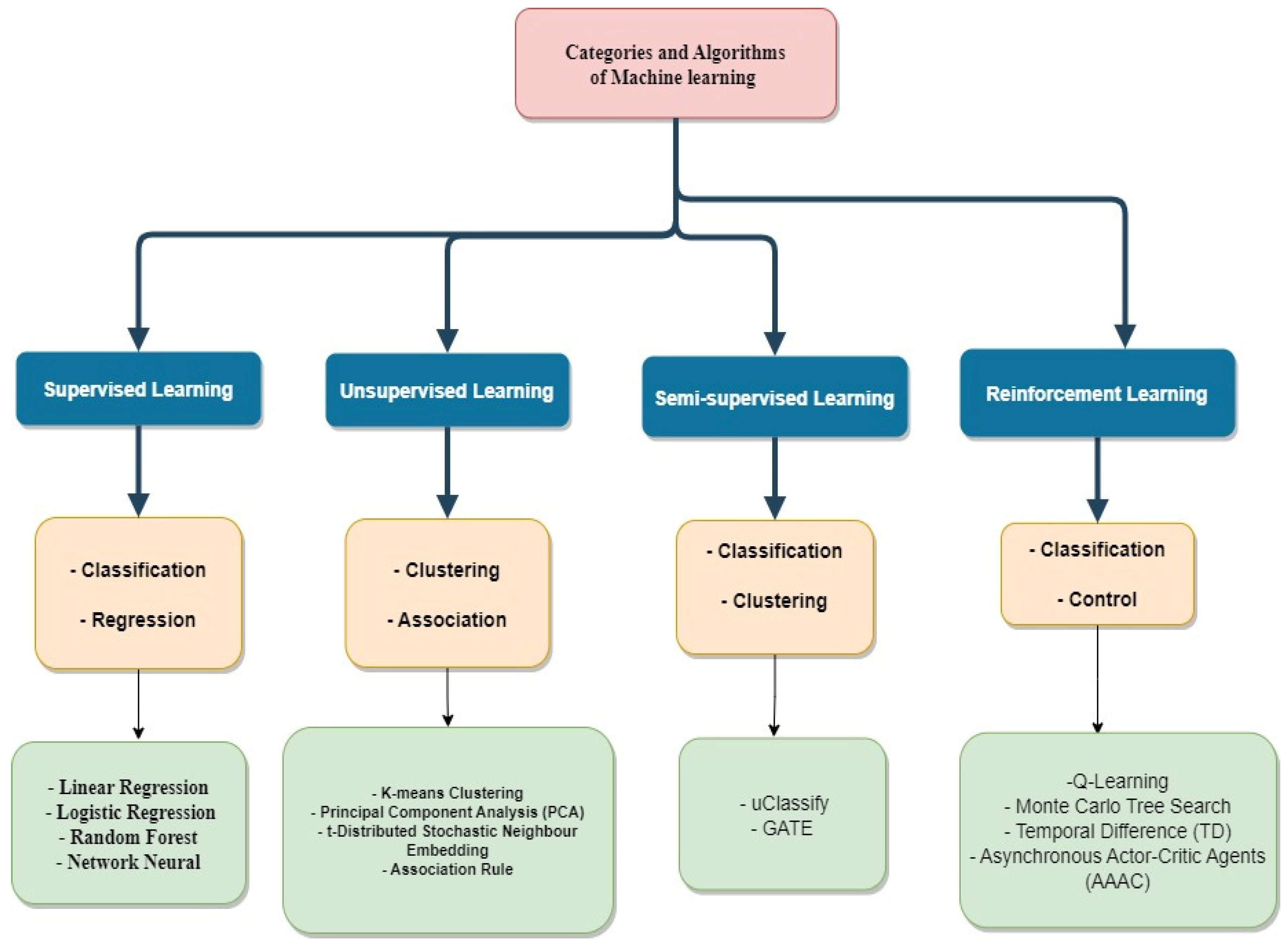
Demystifying Machine Learning: What Happens When Algorithms Learn on Their Own?
Machine learning is a fascinating subset of artificial intelligence that enables systems to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed. At its core, this process involves feeding algorithms large amounts of data, which they analyze to identify patterns and make predictions. The journey begins with data preprocessing, where raw data is cleaned and organized, ensuring that it is suitable for analysis. Following this, algorithms employ various techniques—such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, or reinforcement learning—to extract insights and adapt based on feedback received. Understanding how these methods function can help demystify what happens behind the scenes as algorithms learn on their own.
Once algorithms have been trained on a dataset, their ability to generalize becomes crucial. This is where the concept of overfitting and underfitting comes into play. Overfitting occurs when a model learns the training data too well, including noise and outliers, which can lead to poor performance on new data. On the other hand, underfitting happens when a model is too simplistic, failing to capture the underlying trends in the data. The challenge lies in finding a proper balance, which is achieved through techniques such as cross-validation and regularization. As algorithms navigate this intricate process, they continuously refine their predictions, illustrating the remarkable capability of machine learning to enhance decision-making and solve complex problems independently.
Can Machines Outthink Us? Exploring the Limitations and Potentials of AI Algorithms
As technology continues to advance, the question Can machines outthink us? becomes increasingly relevant. Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms are designed to mimic human reasoning and decision-making processes. However, it is essential to understand that their capabilities are limited by the data they are trained on and the complexity of human emotions and contextual understanding. While AI can process vast amounts of information and identify patterns faster than any human, it lacks the ability to genuinely comprehend subtle nuances and moral implications in the way that humans can. This raises critically important discussions about the real limitations of AI in replicating human thought.
On the other hand, the potential of AI algorithms cannot be ignored. They are transforming industries by enhancing productivity, facilitating data-driven decisions, and optimizing tasks. For instance, AI can automate routine processes and even predict future trends through predictive analytics. However, the question of trust remains prevalent: Can we rely on these algorithms to make decisions that align with human values? As we grapple with this question, it becomes clear that the future of AI lies not in surpassing human intelligence but in creating a collaborative relationship where the strengths of both human and machine intelligence can synergize to lead to better outcomes.